U.S. begins reshaping international trade and its role on global stage
“U.S. policies continue to define the global business landscape through Q1 2025. The implementation and even just the threat of both country- and product-specific trade tariffs on imports to the U.S. – and related counter-tariffs – raise uncertainty and drive expectations of an increase in inflation and government bond yields. The downside risk posed by intensifying trade tariffs to global growth prospects is deepened by the mounting threat of wider trade protectionism and fragmentation, affecting economic relationships between countries and reshaping business supply chains. Intense diplomatic activity related to the Ukraine war and the transformation and potential breaking up of international relations raises uncertainty and risks for corporates, particularly those with a relatively large global footprint, such as those with interconnected markets or highly integrated supply chains. While making sense of today’s uncertain, complex and fast-moving world is becoming increasingly challenging, the environment nevertheless provides businesses with both risks and opportunities for growth.”
Dr. Arun Singh, Global Chief Economist, Dun & Bradstreet.
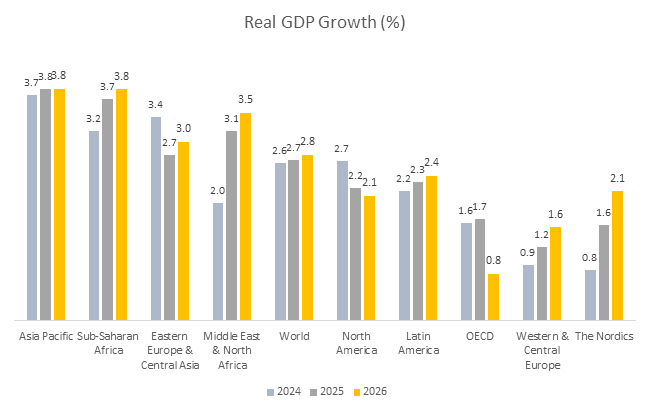
Sources:Haver Analytics; forcasts from Dun & Bradstreet.
Recent Developments
Global
The U.S. is set to introduce 25% product-specific import tariffs on steel and aluminum on March 12, 2025, having already imposed country-specific tariffs on U.S. imports of Canadian and Mexican goods, and an additional 10% tariff on imports from the Chinese Mainland (on top of the 10% tariff imposed in early February). The U.S. has also warned that the EU is to face 25% tariffs on exports to the U.S.
In Germany, the Christian Democratic Union (CDU)-Christian Social Union (CSU) alliance won elections with 28.6% of the vote. The far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD) came second with 20.8%. Friedrich Merz, the CDU leader, will work towards forming a coalition but has signaled that lack of shared values means the AfD will not play a part in this coalition.
EU finance ministers met in mid-March to discuss joint borrowing initiatives targeting new defense spending strategies. This comes in response to escalating security threats from rising geopolitical tensions, which have caused long-dated government bond yields to soar on the expectations of a huge ramp-up in fiscal loosening.
Indian GDP grew 6.2% y/y in real terms during October-December (Q3 FY2024-25). The data precedes this year’s budget and interest rate cuts by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI, the Indian central bank) in February.
Movement in Country Rating & Enviornment Risks
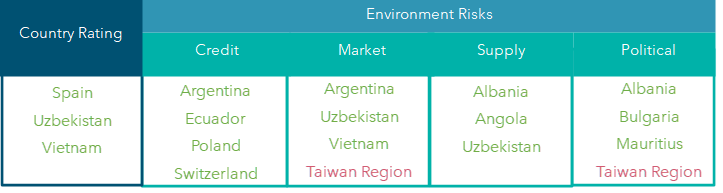
Note: Colors indicate Rating upgrade/Improvement in outlook, Rating downgrade/Deterioration in outlook
North America
The U.S. is set to introduce 25% import tariffs on steel and aluminum on March 12, 2025. The EU has estimated that the hit to its economy may be worth EUR28.0bn (USD29.3bn), though the European Commission is expected to respond with proportionate counter measures. The U.S. is the world’s largest steel importer.
The U.S. has also placed an additional 10% tariff on imports from the Chinese Mainland (on top of the 10% tariff imposed in early February) and has warned that the EU is to face 25% tariffs.
The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) has been scheduled for closure following a near-total freeze on foreign aid by the US government.
The U.S. has announced the suspension of military aid to Ukraine. The U.S. has also opposed a European resolution condemning Russia’s invasion of Ukraine at the UN Security Council, instead introducing a resolution to end the conflict and drafting negotiation proposals for Ukraine. Ukraine has not yet agreed to a U.S. proposal that included the demand for 50% of its rare earth minerals, a value that the U.S. equates with its own military and economic aid to Ukraine.
In February, U.S. tariffs on imports from Canada and, more broadly, Donald Trump’s presidency dominated debates between the candidates competing to become the next Canadian prime minister. The Liberal Party, struggling in the polls since mid-2023, has seen its ratings surge since the departure of Justin Trudeau.
West and Central Europe
In February, federal elections in Germany resulted in a victory for the CDU-CSU union, led by Friedrich Merz. The parties will look to form a coalition with the Social Democratic Party (SPD) by April and must act quickly to address domestic and external issues. Possible policy changes include lower taxes, cuts to regulation, tighter border controls and deeper EU integration.
France has passed its 2025 fiscal budget, easing political turmoil that has engulfed the country since snap elections last year. The budget will create additional friction for businesses, as it includes measures such as corporate income tax surcharges.
The European Commission has unveiled its Clean Industrial Deal, which will maintain previous climate agreements while cutting business regulations to boost the competitiveness of energy-intensive and clean technology sectors.
U.S. President Donald Trump has threatened 25% tariffs on imports from the EU. It is currently unclear if these will apply to certain goods (such as cars) and when they will come into effect. The EU has been working on retaliatory measures, as President Trump has been proposing these tariffs since his inauguration in January.
European leaders are holding a series of meetings in February and March to discuss a revamp of defense policy for the region; this comes following the U.S. and Russia meeting to negotiate a resolution to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Asia Pacific
The U.S. is considering reciprocal tariffs, which could affect major Asian exporters, particularly in the electronics, automotive, and steel industries, leading to potential trade realignments.
The Reserve Bank of India reduced its policy rate by 25bps in February and launched a large-scale liquidity injection program in late January. However, there are indications that liquidity in the banking system remains strained despite these measures.
In January 2025, Indonesia officially became a BRICS member, deepening economic ties with emerging markets and shifting trade and investment priorities.
Thailand adopted the OECD’s 15% global minimum corporate tax effective from January 1, 2025, for multinational corporations with revenue above EUR750m.
In January, Malaysia introduced a law mandating operating licenses for large social media platforms to enhance cybersecurity, protect users, and strengthen regulatory oversight for online messaging and social media services.
In 2024, Singapore’s economy grew 4.4%, supported by strong performances in manufacturing, services, and construction.
East Europe and Central Asia
President Trump has announced a new phase of negotiations with Russia about a Ukraine war ceasefire, following the first round of discussions in February in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. However, a recent disagreement between the U.S. and Ukraine has put the finalization of a draft agreement granting the U.S. access to Ukraine's mineral resources, including rare earth elements, on hold.
European leaders are continuing to convene to address their exclusion from U.S.-Russia peace talks and to emphasize Europe’s role in future security. Meanwhile, after a previously unsuccessful discussion with President Trump, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy is now expressing his willingness to sign a minerals’ deal with the U.S. and take the lead in peace negotiations with Russia.
Russian President Vladimir Putin has emphasized that Europe's participation in Ukraine peace talks will be needed eventually but Moscow first wants to build trust with Washington.
Romania has been admitted to the EU’s Schengen zone, ending long waits on the Romanian border with Hungary.
Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan plan to expand economic cooperation in multiple sectors (trade, water and energy, transport, agriculture, and ecology) and aim to double their mutual annual trade to USD10bn in the coming years.
In late February, Turkmenistan and the Kyrgyz Republic held political consultations in Bishkek, discussing cooperation in trade, economy, investment, transport, logistics, and energy.
In 2025, the Uzbek government announced plans to launch 8,000 projects worth USD14bn to generate 272,000 permanent jobs, attract USD42bn in foreign investment, and boost exports by over USD30bn.
Latin America
Growth in Latin American countries is expected to remain sluggish in 2025 at 2.3%, although up from 2.2% in 2024; however, this contrasts favorably with the weak growth seen during the pre-pandemic years (an average of -0.2% in 2015-19).
Downside risks to growth are materializing with the imposition of unfavorable trade policies, which are likely to impact trade and investment relations.
In January, Mexico hiked tariffs on couriered goods originating from countries with which it does not have a shared international treaty. In early February, Ecuador announced a 27% tariff on all imports from Mexico. The U.S. imposed a 25% tariff on Mexican imports in March, though carmakers were temporarily spared.
In February, the US imposed a 25% tariff on imported steel and aluminum, which will impact Argentina, Brazil and Mexico, as these countries are major suppliers of those commodities to the U.S.
President Trump’s hint about reclaiming control over the Panama Canal has triggered concerns, given that the canal carries approximately 3% of global shipping trade.
Panama will withdraw from the Belt and Road Initiative when its agreement expires in 2026; however, it is unlikely to sever diplomatic ties with the Chinese Mainland, as maintaining the status quo is a key aspect of Panamanian foreign policy.
Middle East and North Africa
A 42-day ceasefire between Israel and Hamas began on January 19, 2025, mediated by Qatar, Egypt, and the U.S. The agreement covers hostage exchanges, increased humanitarian aid, and long-term stability efforts but remains fragile, with multiple instances where it nearly collapsed.
Political and geopolitical risks are elevated but contained. Oil prices are stable and economic growth remains reasonable, shaping a neutral outlook for the region this year.
In February, the Saudi Real Estate Refinance Company raised USD2bn through an international sukuk (Islamic financial certificates similar to bonds) issuance, reflecting strong investor confidence in the Saudi financial sector.
The Abu Dhabi Global Market has introduced a regulatory framework for fiat-referenced digital assets, reinforcing the UAE’s position as a leader in digital finance.
The Nordics
In February, the Nordic-Baltic Eight (a regional cooperation format that includes Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden) issued a joint statement condemning Russia's ongoing military aggression against Ukraine. They pledged to provide more support to Ukraine.
The Nordic Council of Ministers has outlined its political priorities for 2025-30, focusing on making the region the most sustainable and integrated region in the world by 2030. Key areas of focus include addressing geopolitical tensions, the climate crisis, threats to biodiversity, the digital revolution, and ageing populations.
President Trump has expressed interest in the U.S. taking control of Greenland, currently part of Denmark, citing its strategic importance in the Arctic.
Danish Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen has addressed President Trump's renewed interest in acquiring Greenland, emphasizing that the island's future rests with its inhabitants. She has also announced plans to invest USD1.5bn in measures to protect Greenland from external interests.
In February, the Central Bank of Iceland reduced its key interest rate by 50bps to 8%, aiming to support economic activity amid easing inflation and a positive outlook for continued disinflation in the coming months.
Sub-Saharan Africa
The continuing conflict between the Sudanese Armed Forces and the Rapid Support Forces could potentially lower growth rates in the region as the disruption affects business operations.
The M23 rebels have taken control of the key mining cities – Rubaya and Goma – in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), which can affect tantalum supply. The DRC supplies ~40% of the global tantalum requirement.
Nigeria has revised its base year to 2024 from 2009, which led inflation to fall to 24.48% y/y in January 2025, from 34.4% in December 2024.
Zambia has removed the 15% export tariffs on gemstones. This will help increase the competitiveness of the country’s exports.
After a report by Senegal’s Court of Auditors, the central government’s debt as a percent of GDP has been revised to 99.6% for 2023, from 77.4%, and the fiscal deficit has been revised to 12.9% of GDP. These developments could derail the country’s GDP growth, which was 7% in Q3 2024.
The recent Expropriation Act of 2024 by South Africa could impact the renewal terms for the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) for the country. Exports from South Africa to the U.S. under the act increased 14% y/y in 2024.
The U.S. government’s near-total freeze on funding to the USAID and scheduled closure of the agency could lead to widespread unemployment and affect health infrastructure across the region.
Movement in Risk Dimensions
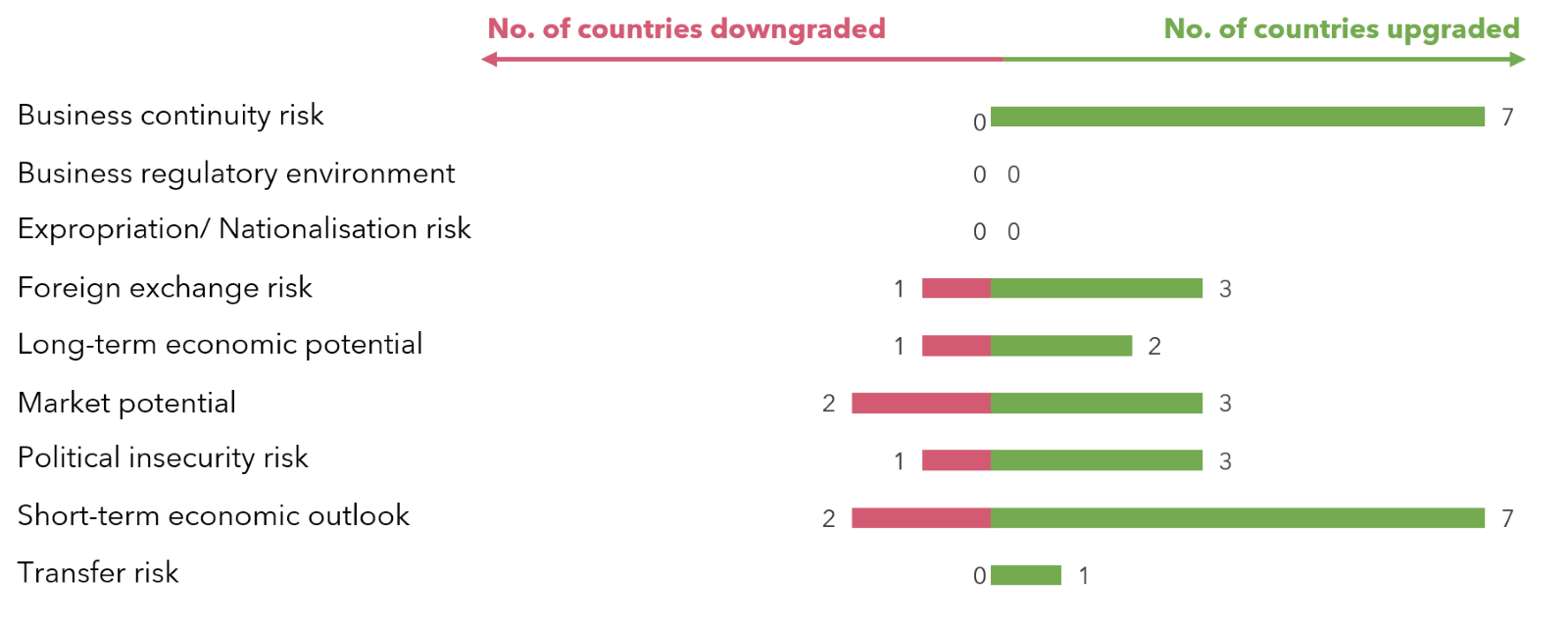
Sources: Dun & Bradstreet.
How Dun & Bradstreet Can Help
Dun & Bradstreet's Country Insight Solutions provide forecasts and business recommendations for 132 economies, allowing businesses to monitor and respond to economic, commercial, and political risks.
To learn more, visit dnb.com/country-insight
